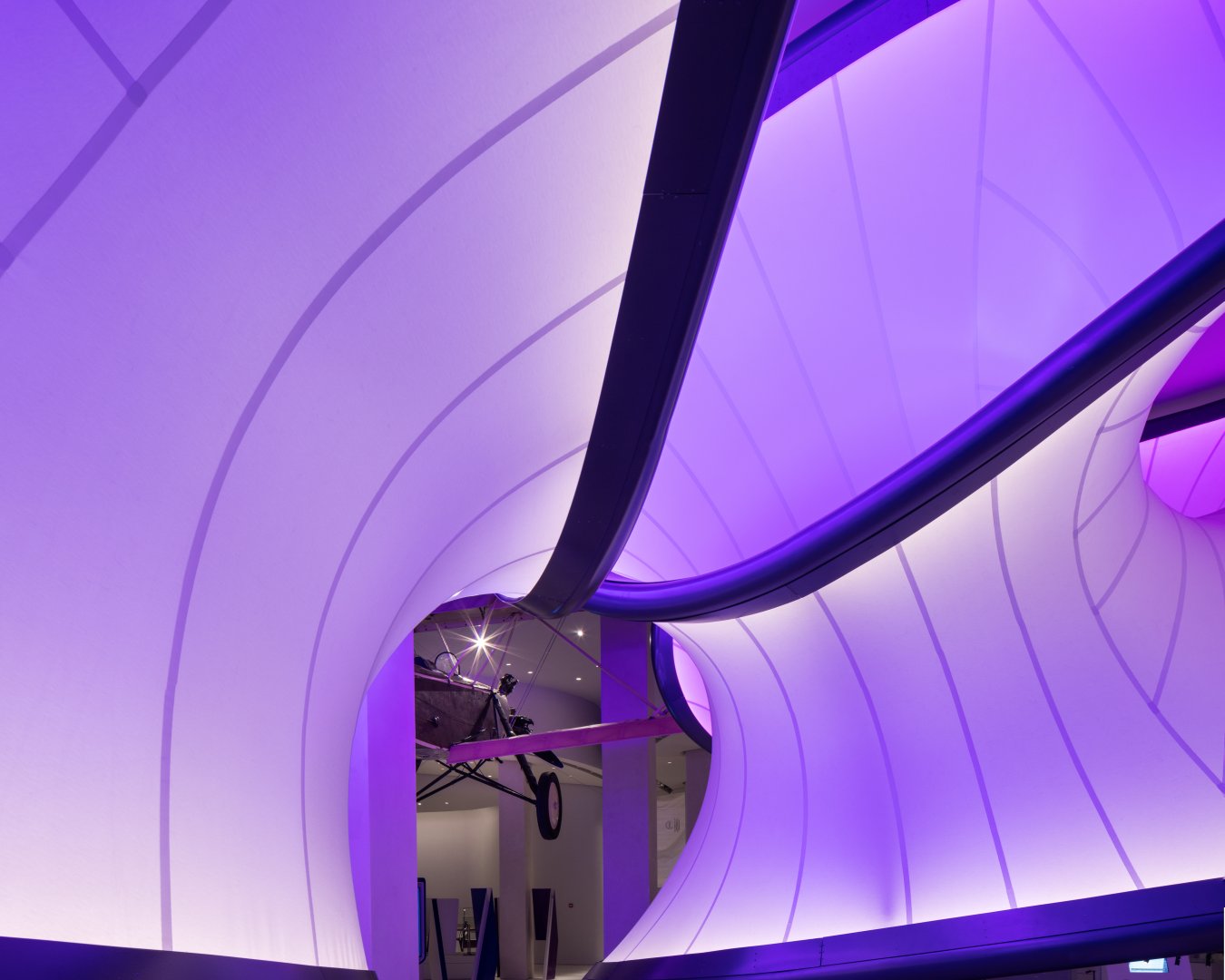
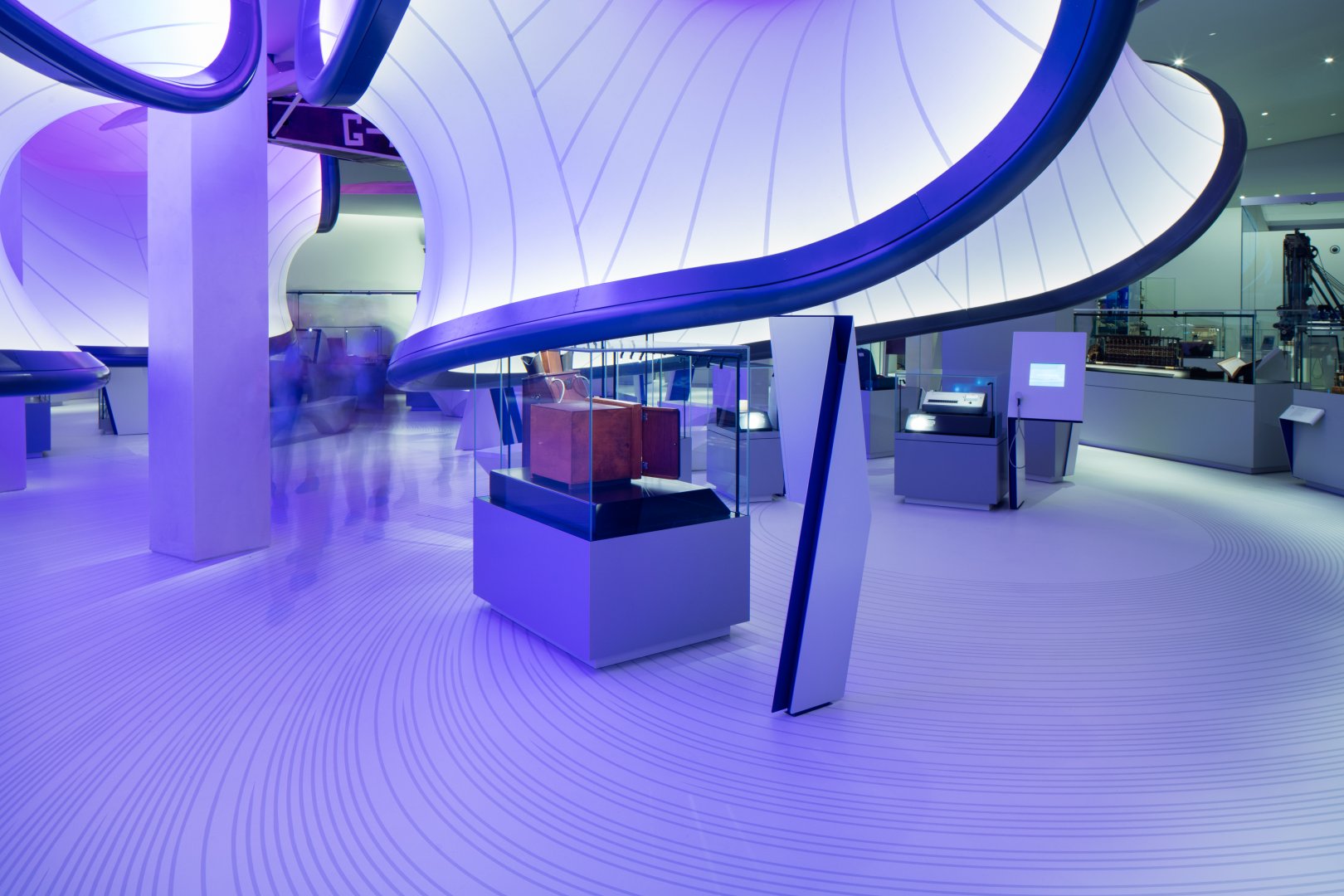
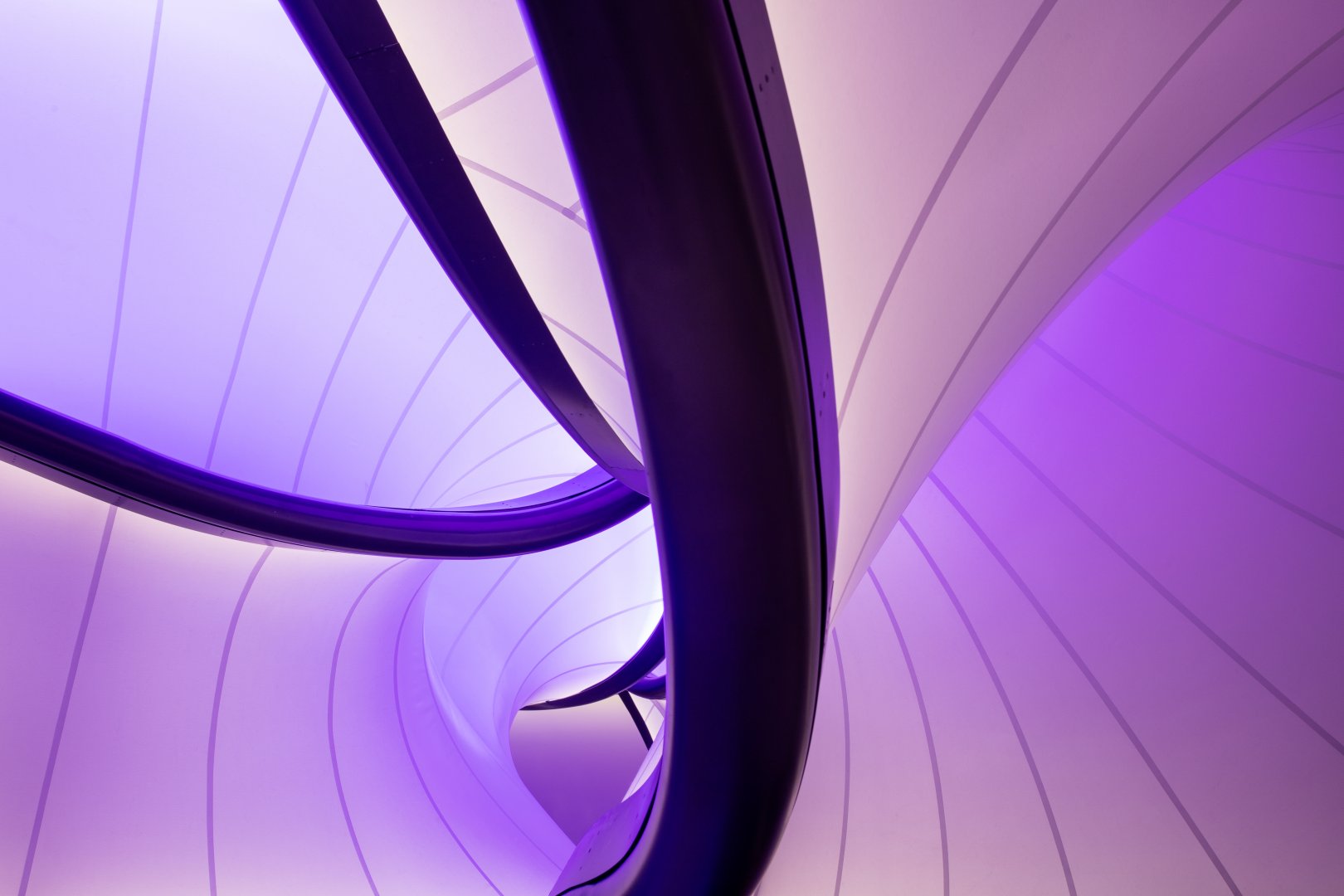
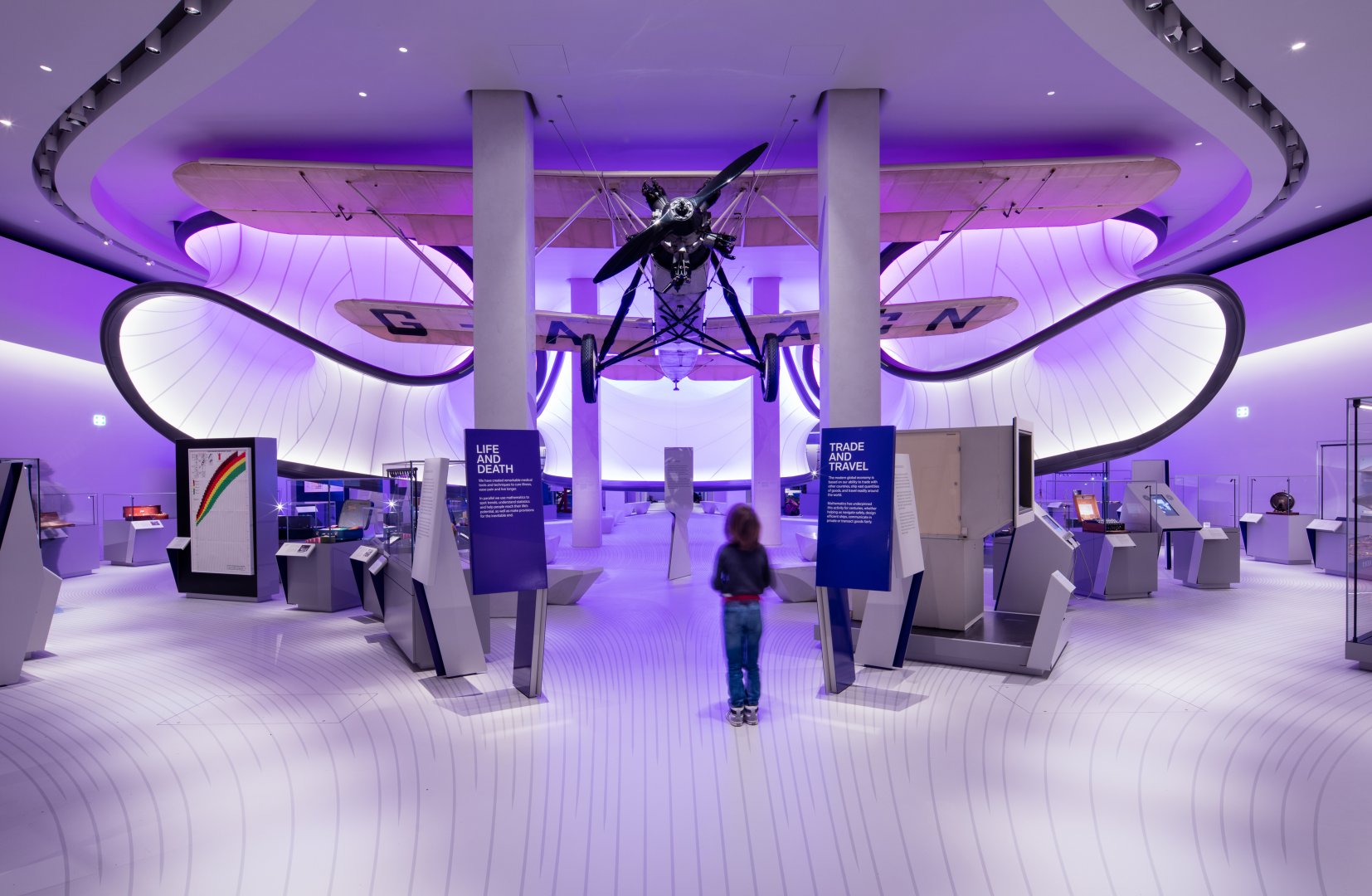
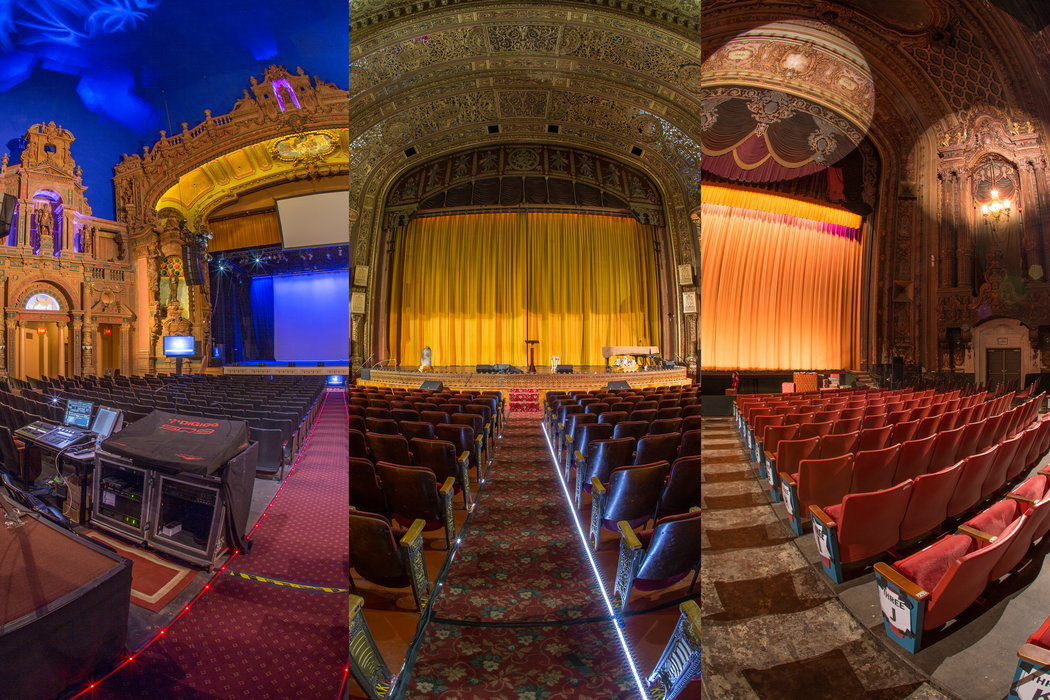
Museums like the Guggenheim and the Louvre are ingrained in our culture and are best known for their impressive collections and beautiful architecture. These institutions often make it onto top museum lists, and for good reason. People love them, but I’m here to introduce you to some lesser-known, but equally noteworthy museums that are architectural marvels in their own right. From science and technology to art and history, these modern galleries from around the world are works of art that you can admire without even setting foot inside.
THE ROYAL ONTARIO MUSEUM in Toronto, Ontario
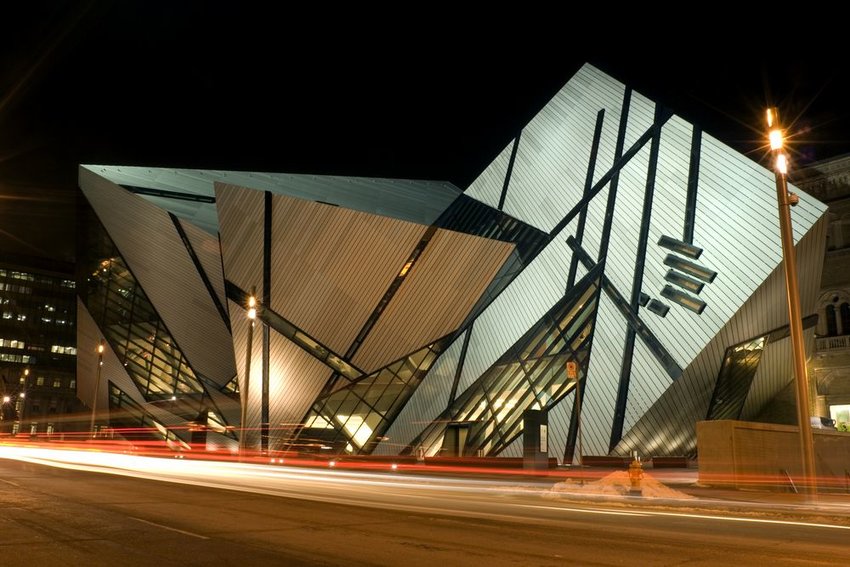

Visit the largest museum in Canada during your next trip to Toronto. The Royal Ontario Museum features exhibits of art, world culture, and natural history and attracts more than one million visitors every year. The historical buildings of the existing structure are complemented by a bold new façade of prismatic glass and metal. According to Studio Libeskind, the architectural firm in charge of the project, the crystal-like atriums presented unique design challenges making it “among the most complicated construction projects in North America.” Besides the impressive multi-million dollar expansion, other reasons to visit include the museum’s vast collection of archaeological specimens as well as its array of design and art pieces.
LOUIS VUITTON FOUNDATION in Paris, France
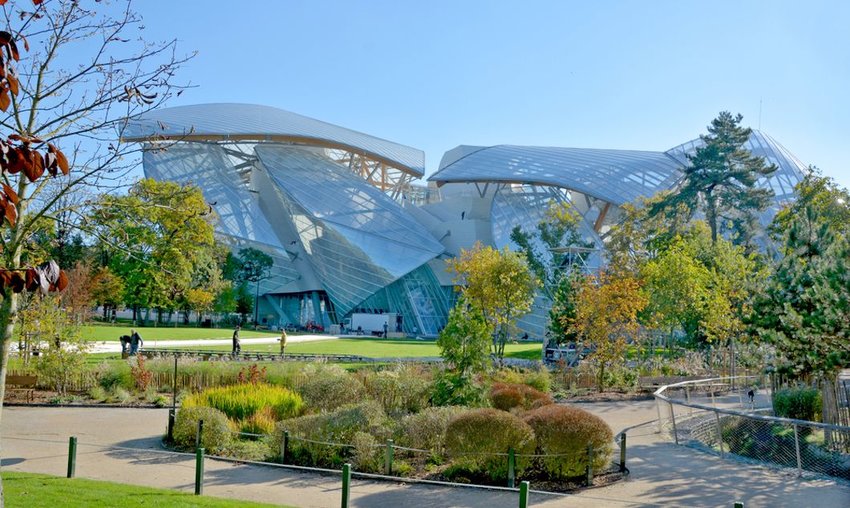

Since 2014, the Louis Vuitton Foundation’s art museum in Paris has introduced visitors to exhibitions promoting modern and contemporary artistic creation. The museum is a production of world-renowned architect Frank Gehry. Its design presented builders with unprecedented technical challenges, namely its clustered white blocks (that the team called icebergs) and twelve glass “sails” supported by wooden beams. The interior design is just as impressive as the exterior — opening up to vast, lofty halls with plenty of natural light. The glass walls and ceilings not only provide epic views of downtown Paris from top floors but also play with the museum’s artwork through light, mirrors, color, and more.
MILWAUKEE ART MUSEUM in Milwaukee, Wisconsin

Located on the coast of Lake Michigan in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin is one of the largest art museums in the United States. The Milwaukee Art Museum is home to nearly 25,000 works of art including an extensive Georgia O’Keeffe collection. The museum is comprised of three buildings including the War Memorial Center, Cudahy Gardens, and the Quadracci Pavilion — the iconic glass building that opened in 2001. The 90-foot glass ceiling features a 217-foot moveable, wing-like screen that unfolds twice daily. Called the Burke Brise Soleil, these “wings” open at 10 in the morning, flap at noon, and close when the museum closes. The pedestrian suspension bridge conveniently connects the museum to the city.
MIHO MUSEUM in the Koka Forest, Kyoto, Japan

Located in the dense forest of Koka near Kyoto, Japan, the MIHO Museum offers visitors a unique architectural experience that blends manmade structures and natural surroundings. Designed by famous architect I. M. Pei, the steel and glass structures of the museum were designed to contrast against the panoramic views of the mountains and valleys below. Visitors first walk through an arched tunnel to reach the museum entrance, which is one of the only above-ground structures in the complex. In an effort to preserve the natural environment, about 80% of the museum is underground. The exhibits at MIHO frequently change with a focus on ancient works from the Egyptians, Romans, and Asian cultures.
MUSEO SOUMAYA at PLAZE CARSO in Mexico City, Mexico

The Museo Soumaya has become a highlight of Mexico City’s art scene with its shimmering, anvil-shaped exterior and impressive art collection ranging from MesoAmerican history to modern day. While the museum technically consists of two buildings, the most popular is the new structure at Plaza Carso, where the primary museum collection was moved in 2011. This nine-story building made of 16,000 aluminum hexagons was designed by Fernando Romero, who commonly focuses on fluidity in his designs. As one of the most-visited museums in Mexico, it’s no surprise that its list of A-list displays is lengthy. Don’t miss the vast collection of artwork by Rodin including the famed sculpture “The Thinker” — a permanent exhibit here.
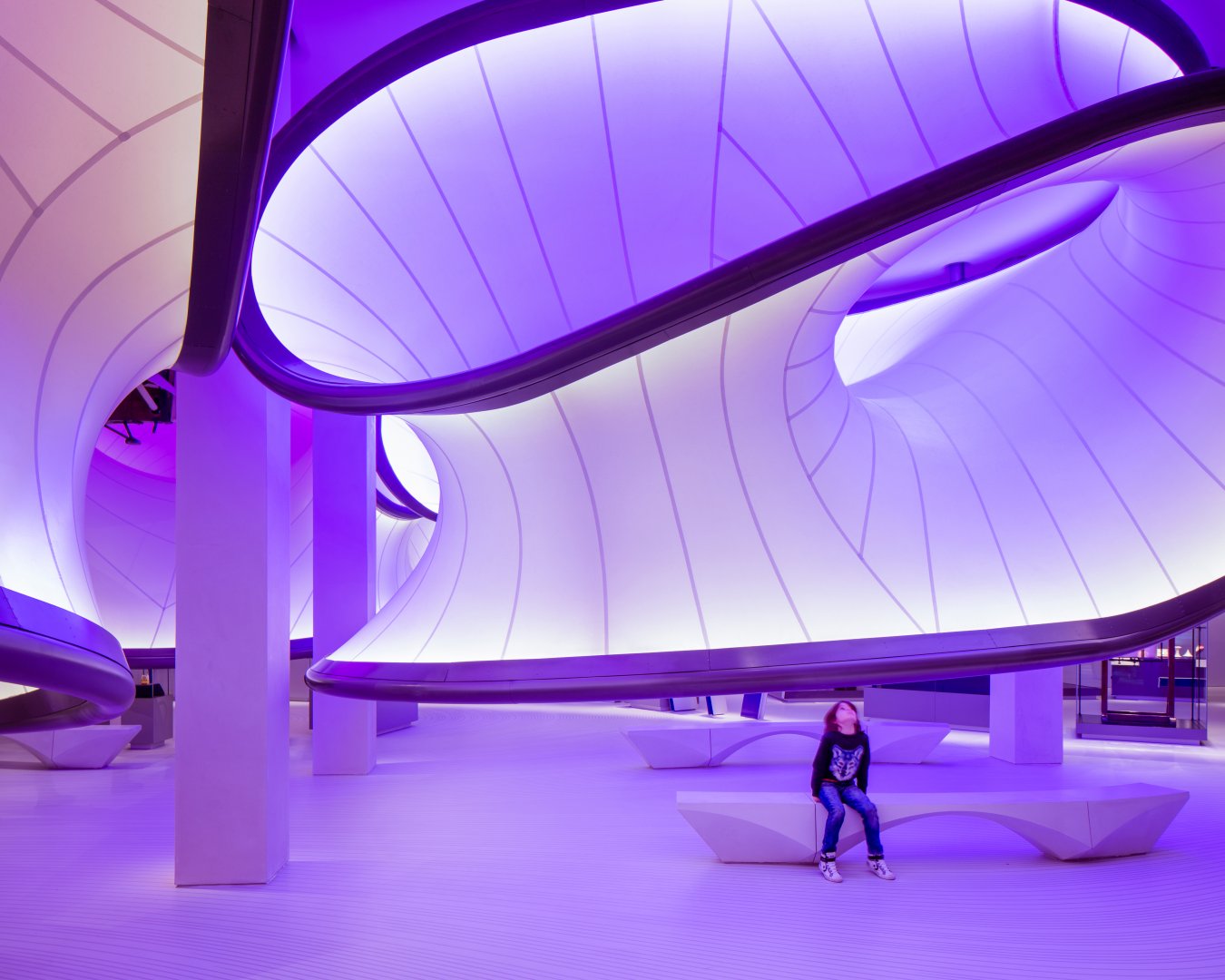
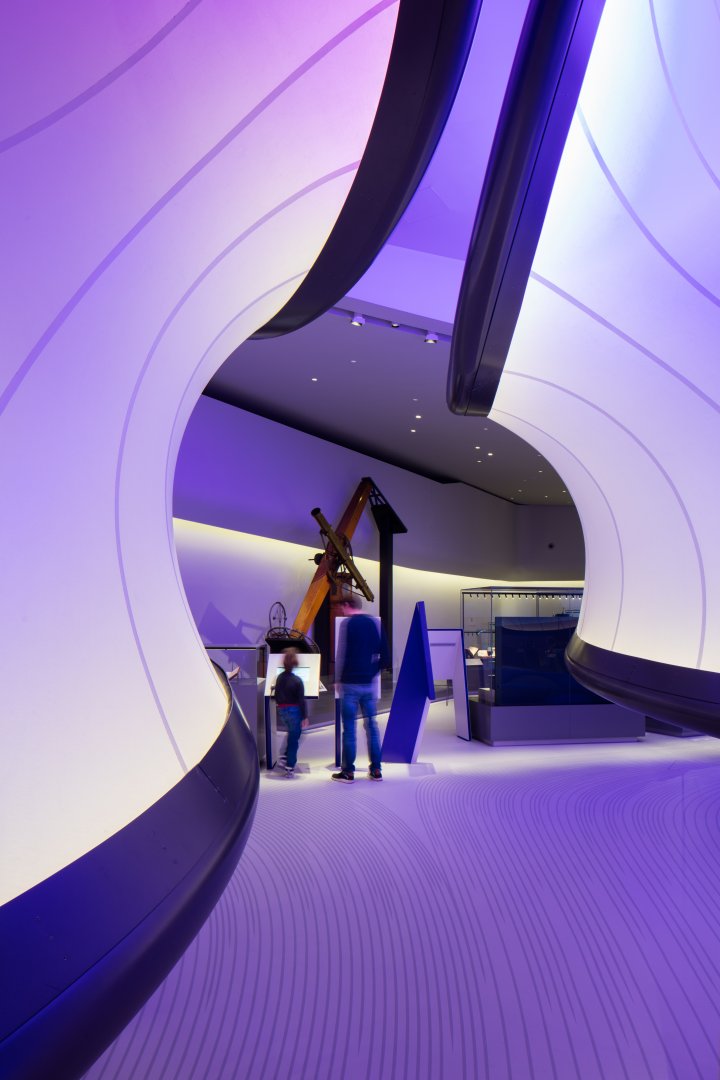
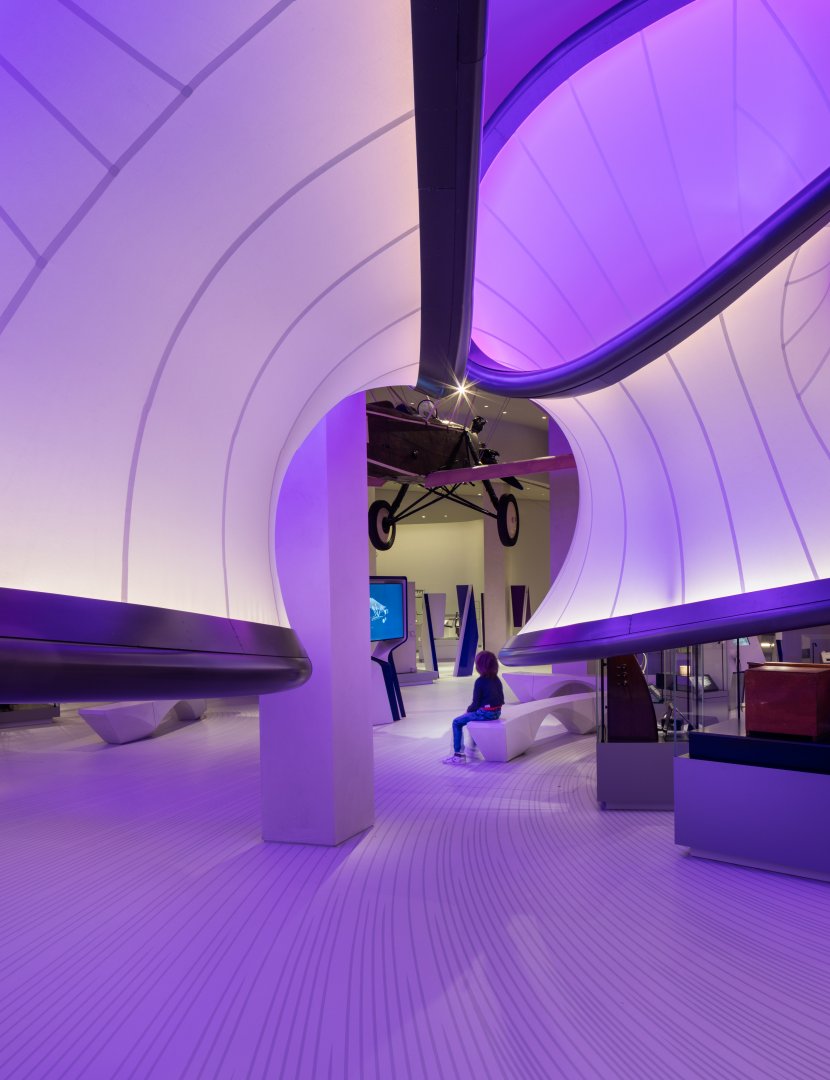
MAXXI NATIONAL MUSEUM IN ROME, ITALY

The MAXXI National Museum of 21st Century Arts focuses on contemporary art and architecture. Upon opening in 2010, this museum designed by architect Zaha Hadid received a Stirling Prize for architecture by the Royal Institute of British Architects. The massive complex consists of two sections — “MAXXI Art” and “MAXXI Architecture” — along with an outdoor courtyard for large-scale works of art. The interior stairways and walking paths overlap to create an exciting and dynamic environment for visitors. The museum’s most prominent architectural features are its curved, concrete walls and suspended, black staircases. Its interior colors and structures are a nod to the overarching theme of the museum — to promote contemporary art and architecture.
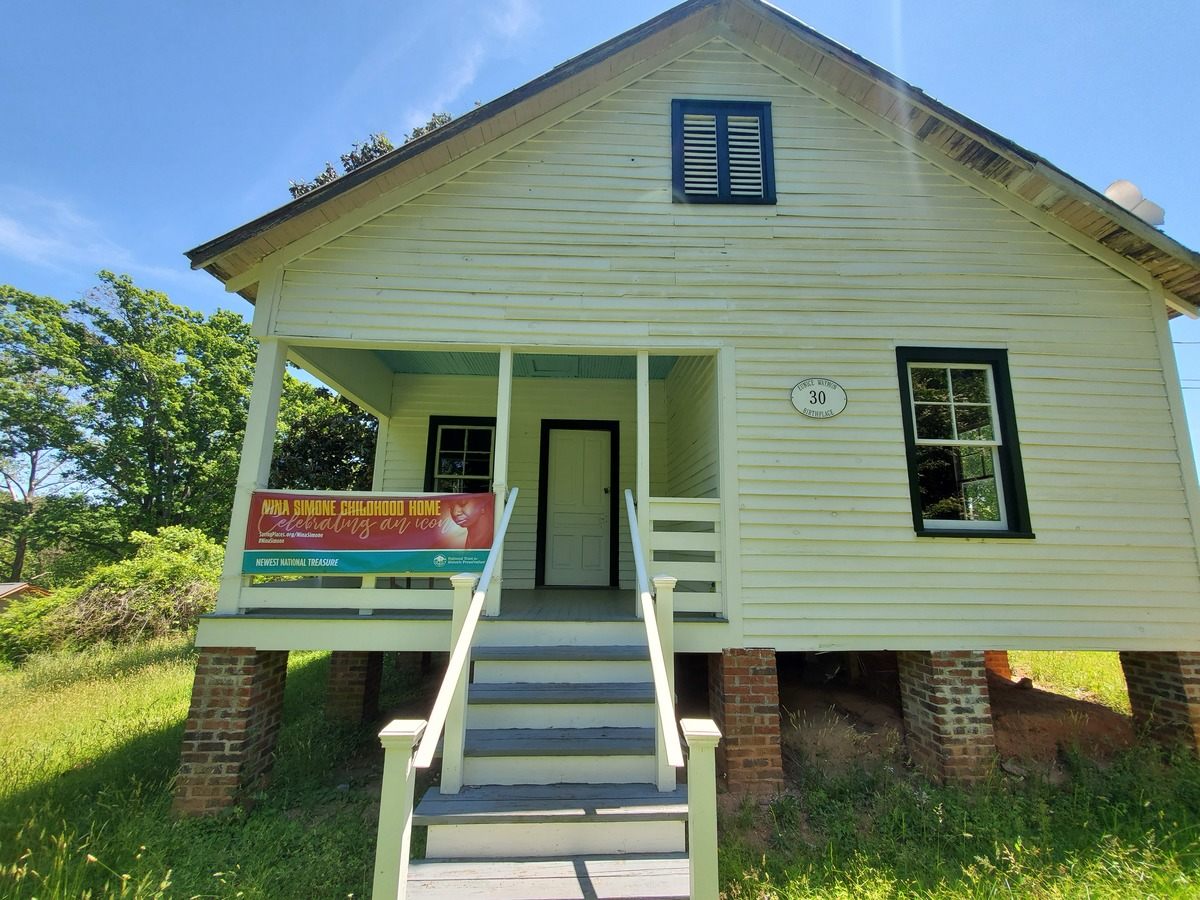
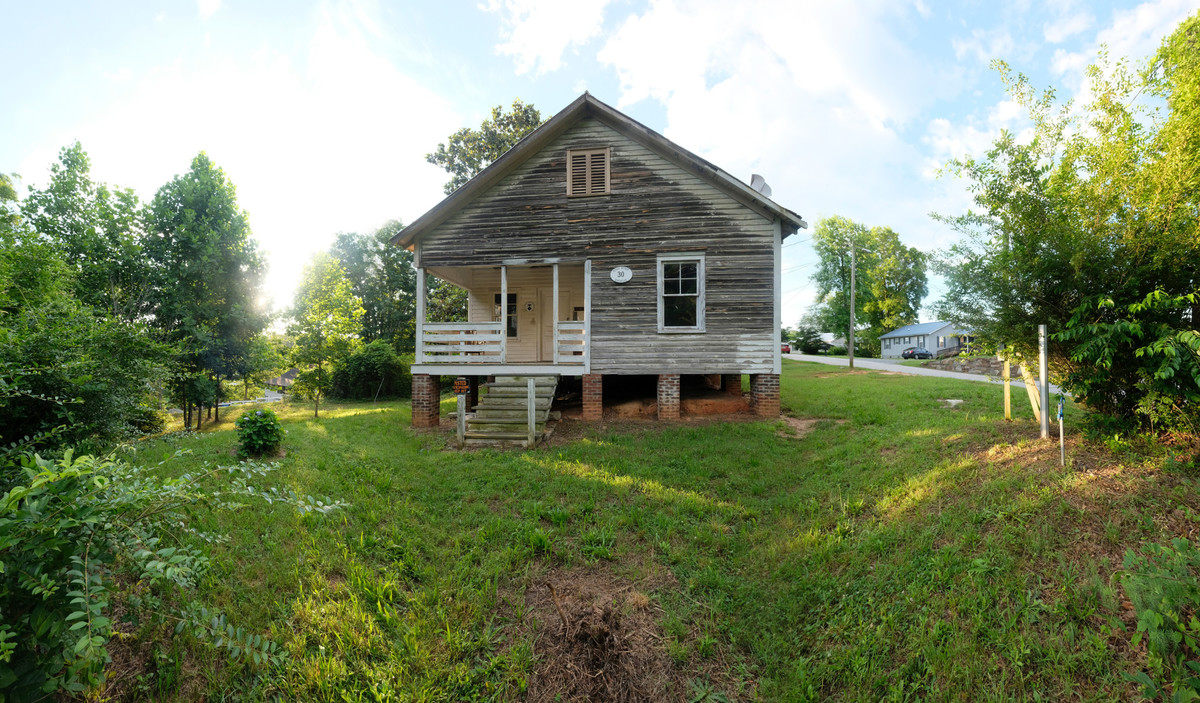 The home, a three-room, 660-square-foot clapboard pier and beam house, is where Simone—born Eunice Waymon—taught herself to play piano by ear at the age of three. It had been vacant for 20 years, until going on the market in December 2016. That is when artist Adam Pendleton received an email from Laura Hoptman, a curator of contemporary art at The Museum of Modern Art, letting him know that Simone’s childhood home was for sale. When Hoptman mentioned that she had also emailed artist Rashid Johnson, Pendleton had an epiphany. “I had an aha moment and said, ‘Wait a minute, we could purchase this house together. It could be a collective act, a collective gesture.’” With Johnson on board, they recruited artists Ellen Gallagher and Julie Mehretu. “We both agreed that it would be a more meaningful gesture if other artists were involved,” he says. Together the artists purchased the home for $95,000 in March 2017.
The home, a three-room, 660-square-foot clapboard pier and beam house, is where Simone—born Eunice Waymon—taught herself to play piano by ear at the age of three. It had been vacant for 20 years, until going on the market in December 2016. That is when artist Adam Pendleton received an email from Laura Hoptman, a curator of contemporary art at The Museum of Modern Art, letting him know that Simone’s childhood home was for sale. When Hoptman mentioned that she had also emailed artist Rashid Johnson, Pendleton had an epiphany. “I had an aha moment and said, ‘Wait a minute, we could purchase this house together. It could be a collective act, a collective gesture.’” With Johnson on board, they recruited artists Ellen Gallagher and Julie Mehretu. “We both agreed that it would be a more meaningful gesture if other artists were involved,” he says. Together the artists purchased the home for $95,000 in March 2017.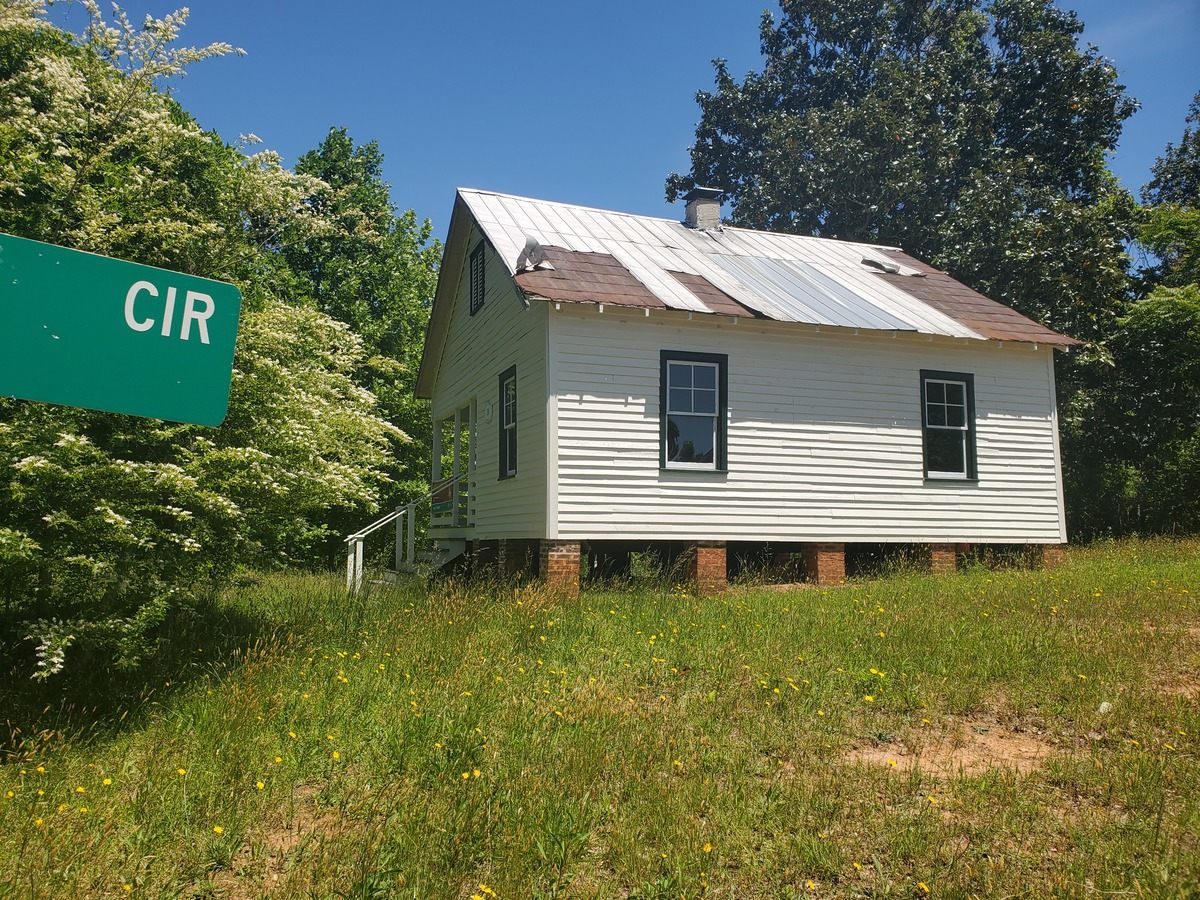
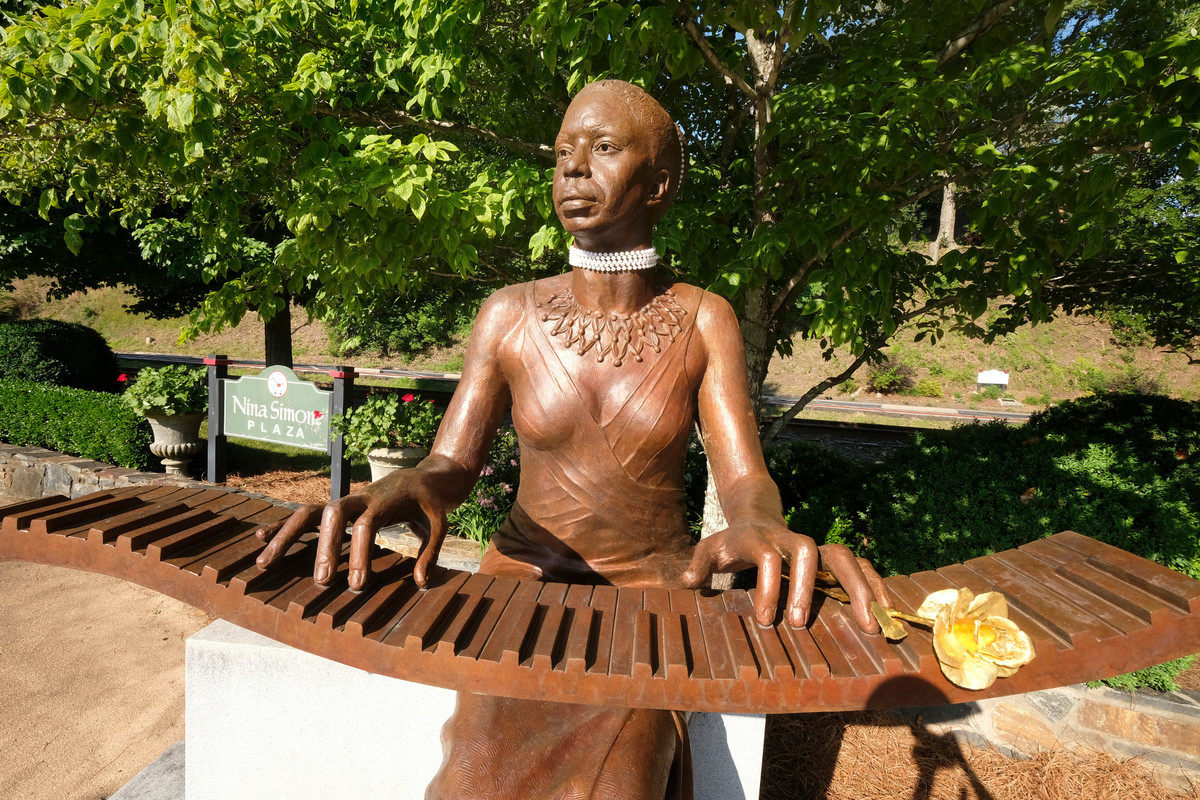 As a young girl, Simone accompanied her mother’s sermons and the church choir on the piano during services. After hearing Simone, then age 6, accompany the community choir at the Tryon Theater, two women convinced her mother she needed formal piano lessons. One of the women, Mrs. Muriel Mazzanovich, was a local piano teacher. She taught Simone at her house in Tryon for the next four years and organized the Eunice Waymon Fund to raise money for Simone to continue her training after she left for high school.
As a young girl, Simone accompanied her mother’s sermons and the church choir on the piano during services. After hearing Simone, then age 6, accompany the community choir at the Tryon Theater, two women convinced her mother she needed formal piano lessons. One of the women, Mrs. Muriel Mazzanovich, was a local piano teacher. She taught Simone at her house in Tryon for the next four years and organized the Eunice Waymon Fund to raise money for Simone to continue her training after she left for high school.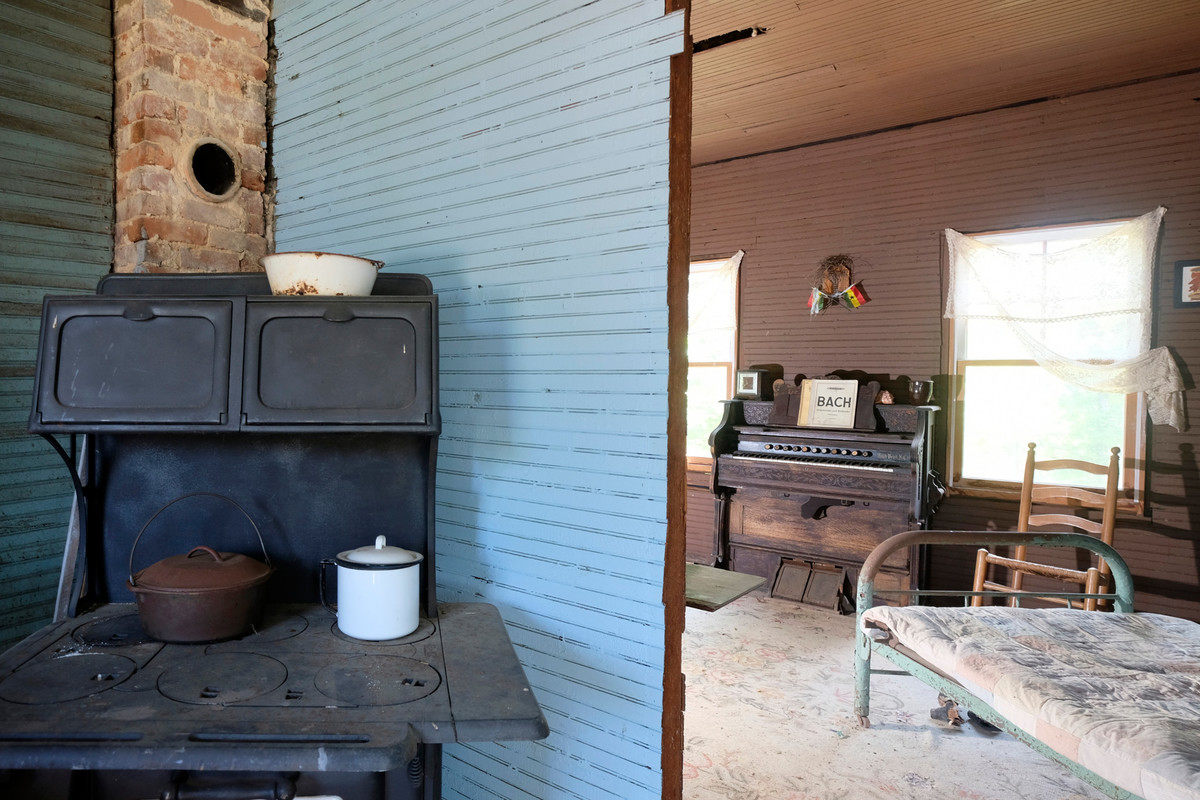 To thank those who supported the fund, Simone performed her debut recital at the Tryon Library in 1943 at age 11. However, living in a Jim Crow-segregated South, Simone’s parents were forced to give up their seats for white audience members when they arrived at the library. Even then a fierce defender of what she believed to be right, Simone refused to play until her parents were returned to their rightful place in the front row.
To thank those who supported the fund, Simone performed her debut recital at the Tryon Library in 1943 at age 11. However, living in a Jim Crow-segregated South, Simone’s parents were forced to give up their seats for white audience members when they arrived at the library. Even then a fierce defender of what she believed to be right, Simone refused to play until her parents were returned to their rightful place in the front row.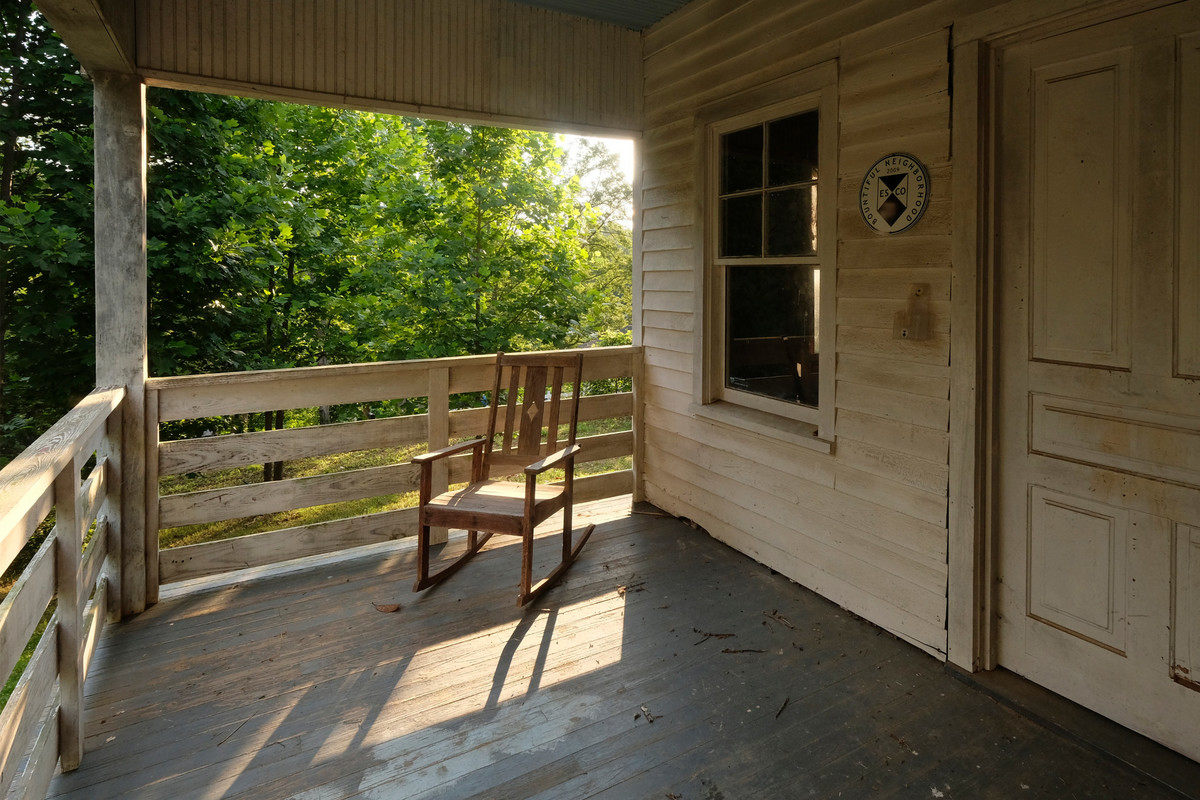 Simone’s piano education continued with the aid of the Eunice Waymon Fund, while she attended an all-girls boarding school in Asheville, North Carolina. Following graduation, she moved to New York City in 1950 to attend a summer program at Julliard with plans to apply for a scholarship at the Curtis Institute of Music in Philadelphia; however, she didn’t receive the scholarship or admittance to Curtis—allegedly due to her race. Simone instead worked odd jobs before returning to music as an accompanist and private teacher. Eventually, she began playing piano and singing at a bar in Atlantic City. There, Simone changed her name, and her career as the High Priestess of Soul took shape.
Simone’s piano education continued with the aid of the Eunice Waymon Fund, while she attended an all-girls boarding school in Asheville, North Carolina. Following graduation, she moved to New York City in 1950 to attend a summer program at Julliard with plans to apply for a scholarship at the Curtis Institute of Music in Philadelphia; however, she didn’t receive the scholarship or admittance to Curtis—allegedly due to her race. Simone instead worked odd jobs before returning to music as an accompanist and private teacher. Eventually, she began playing piano and singing at a bar in Atlantic City. There, Simone changed her name, and her career as the High Priestess of Soul took shape. Much later in her career, Simone returned to Tryon after she had just spent several years living in France and touring Europe. By this point, the artist had built a career, as well as a reputation for expressing her views on civil rights and the racial injustice experienced by African Americans through original songs and covers such as Mississippi Goddam, I Wish I Knew How it Would Feel to be Free, and Four Women.
Much later in her career, Simone returned to Tryon after she had just spent several years living in France and touring Europe. By this point, the artist had built a career, as well as a reputation for expressing her views on civil rights and the racial injustice experienced by African Americans through original songs and covers such as Mississippi Goddam, I Wish I Knew How it Would Feel to be Free, and Four Women.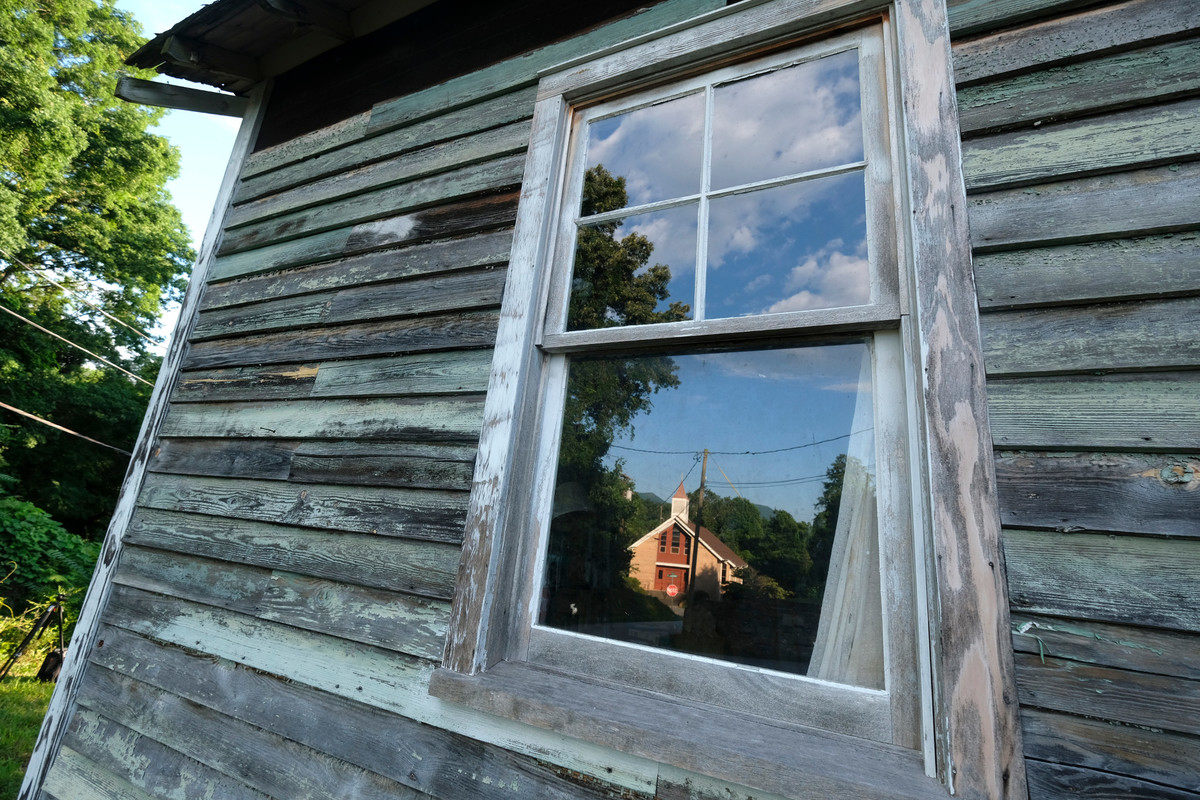 Throughout her career, Simone exhibited musical genius that couldn’t be denied or ignored. She spoke and sang about topics like standards of beauty for black women, oppression, and righteous anger motivated by hundreds of years of slavery and systemic racism. She traveled the world and performed for over four decades, often following momentous historic events like the Selma to Montgomery March and Dr. King’s assassination. She was, in short, a motivating figure for audiences around the world.
Throughout her career, Simone exhibited musical genius that couldn’t be denied or ignored. She spoke and sang about topics like standards of beauty for black women, oppression, and righteous anger motivated by hundreds of years of slavery and systemic racism. She traveled the world and performed for over four decades, often following momentous historic events like the Selma to Montgomery March and Dr. King’s assassination. She was, in short, a motivating figure for audiences around the world.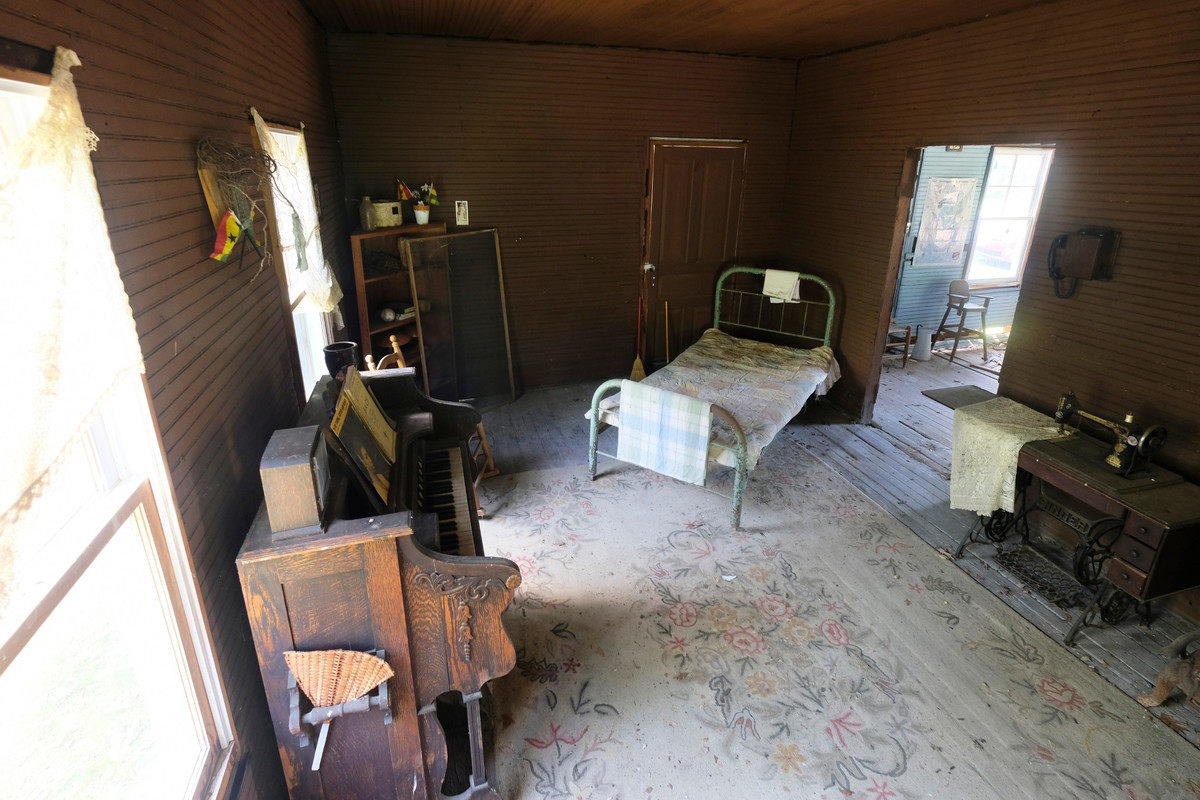
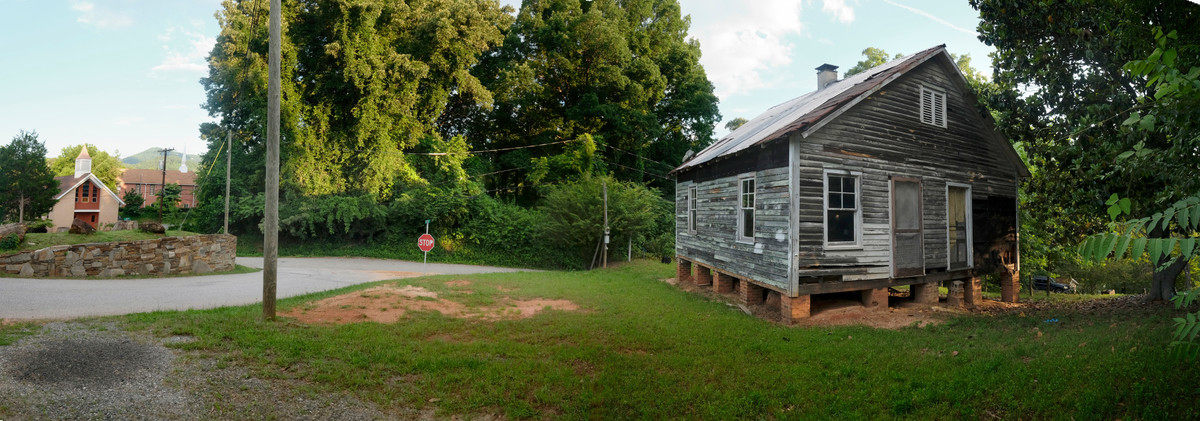 Like Simone, each artist finds ways to connect their work to African American identity and history. Pendleton uses language to re-contextualize history through re-appropriated images. Johnson’s work combines “racial and cultural identity, African American history, and mysticism,” according to his biography on Artsy. Gallagher reinterprets advertisements for products targeted towards African Americans. Mehretu creates renderings of urban grids to reexamine cultural definitions of place. The artists plan to apply their collective artistic vision to reinterpret Simone’s home into something that reflects her dynamic, complex legacy, but they cannot do it alone.
Like Simone, each artist finds ways to connect their work to African American identity and history. Pendleton uses language to re-contextualize history through re-appropriated images. Johnson’s work combines “racial and cultural identity, African American history, and mysticism,” according to his biography on Artsy. Gallagher reinterprets advertisements for products targeted towards African Americans. Mehretu creates renderings of urban grids to reexamine cultural definitions of place. The artists plan to apply their collective artistic vision to reinterpret Simone’s home into something that reflects her dynamic, complex legacy, but they cannot do it alone.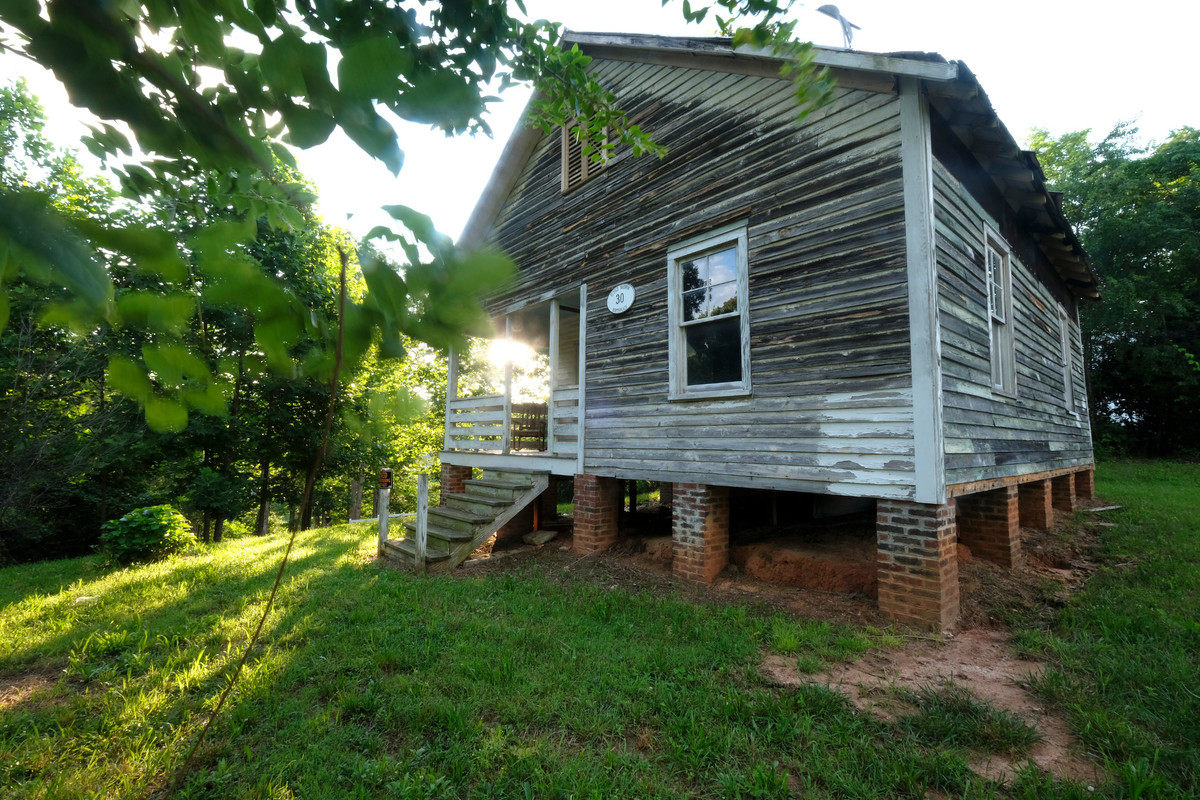 With leadership and guidance from the four artists, the National Trust—along with the Nina Simone Project, World Monuments Fund, and North Carolina African American Heritage Commission—is working to preserve Simone’s Tryon home. The National Trust will develop a rehabilitation plan that aligns with the home’s potential future use; identify future ownership and stewardship models for the site; and create additional protections to ensure that this symbol of Simone’s early life and legacy will endure for generations to come.
With leadership and guidance from the four artists, the National Trust—along with the Nina Simone Project, World Monuments Fund, and North Carolina African American Heritage Commission—is working to preserve Simone’s Tryon home. The National Trust will develop a rehabilitation plan that aligns with the home’s potential future use; identify future ownership and stewardship models for the site; and create additional protections to ensure that this symbol of Simone’s early life and legacy will endure for generations to come.